打开微信,使用扫一扫进入页面后,点击右上角菜单,
点击“发送给朋友”或“分享到朋友圈”完成分享
本系列文章介绍优化YOLOv4网络的整个流程,涵盖了 BangC 算子开发,TensorFlow 自定义算子的注册及添加,PB模型的算子替换和性能精度验证。
实验环境:
MLU270 v1.4.0 release
Cambricon-Tensorflow 1.14
目录
1.PB模型的分析
2.Mish bangC算子的开发、精度验证与性能测试
3.TensorFlow 自定义算子的集成
4.PB网络模型的大算子替换
5.单算子与整体网络的精度验证
PB模型的分析
通过 darknet yolov4 weights 转换成 pb 模型后,利用开源模型可视化软件Netron查看,其中mish 算子的构成如下:
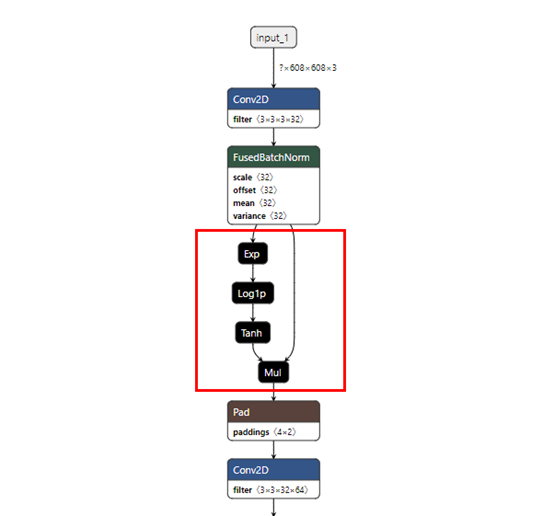
在 yolov4 中,需要运用到 72 个 mish 算子,而TF中暂时没有mish算子的实现,只能用 Exp+Log1p+Tanh+Mul 进行拼凑,然而在MLU270/220的架构下,这种拼凑算子形式会在IO上损耗资源,影响性能,所以全部替换成Mish大算子会有可观的性能提升。
Mish bangC算子的开发、精度验证与性能测试
设计原理:
1. Mish 算子属于激活算子,输入输出均为1维,所以可以将数据做平坦后输出,再再Bangc 里面进行数据分块运算;
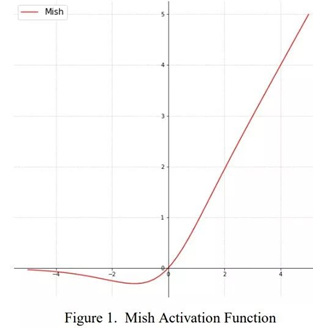
2. Mish算子的公式如图xx,bangc中可以使用 __bang_active_exp、__bang_active_log、__bang_active_tanh、__bang_mul 进行拼凑;

3. 数据分块计算
假设输入为长度为1000000的数据,自定义的数据分块尺寸为12800,先进行的是每个ipu core 的分块,将数据分成16+1份,其中16份的长度相同,剩下的对128向上取整;
然后是对每个ipu core 上的那份数据进行分块,每份长度为12800,剩下的对128向上取整;
这时候完成了数据分块,先对ipu core 上每份12800大小的数据进行多核计算,然后是对每个ipu core 上余下的进行计算,最后是对16份ipu core 分块时余下的进行单核计算;
代码实现:
BangC Mish 算子实现和单元测试,主要对单算子的实现、精度调试和性能评估:
__mlu_entry__ void MishKernel_MLU270(half* input_data_, half* output_data_, int input_size){
struct timeval start;
struct timeval end;
gettimeofday(&start, NULL);//计算算子时间
__nram__ half nram_input[MISH_SIZE];
__nram__ half tmp0[MISH_SIZE];
uint32_t num_total = input_size;
// uint32_t data_count = data_count_/ sizeof(half);
uint32_t num_per_core = num_total / taskDim;
uint32_t rem_for_all = num_total % taskDim;
uint32_t align_rem_for_all = alignUp(rem_for_all,128 );
uint32_t dealsize = MISH_SIZE;
uint32_t repeat = num_per_core / dealsize;
uint32_t rem = num_per_core % dealsize;
uint32_t align_rem = alignUp(rem, 128);
for (int i = 0; i 0){ //最后利用core0来计算剩下的数据块
if (taskId == 0){
__memcpy(nram_input, input_data_ + taskDim * num_per_core , rem_for_all * sizeof(half),GDRAM2NRAM);
//__bang_half2float(nram_input_fp32,nram_input,dealsize);
__bang_active_exp(tmp0,nram_input,align_rem_for_all);
__bang_add_const(tmp0,tmp0,1.0,align_rem_for_all);
__bang_active_log(tmp0,tmp0,align_rem_for_all);
__bang_active_relu(tmp0,tmp0,dealsize);
__bang_active_tanh(tmp0,tmp0,align_rem_for_all);
__bang_mul(tmp0,nram_input,tmp0,align_rem_for_all);
//__bang_float2half_rd(nram_input,tmp0,dealsize);
__memcpy(output_data_ + taskDim * num_per_core , tmp0 , rem_for_all*sizeof(half),NRAM2GDRAM);
}
}
__sync_all();//同步
//计算耗时
gettimeofday(&end, NULL);
uint32_t time_usec = (uint32_t)end.tv_usec - (uint32_t)start.tv_usec;
printf("Hardware Total Time: %u us\n", time_usec);
}
int main() {
const int data_count = DATA_COUNT*BATCH_SIZE;
int batch_num_ = BATCH_SIZE;
int core_num_ = NUM_MULTICORE;
float* data = (float*)malloc(data_count * sizeof(float));
float* cpu_out = (float*)malloc(data_count * sizeof(float));
for (int i = 0; i<DATA_COUNT;i++ ){
data[i] = (rand() % 100) / 50.0; //随机生成数据
}
mish_cpu(data, cpu_out, data_count); //计算CPU
cnrtInit(0); //初始化设备
cnrtDev_t dev;
cnrtGetDeviceHandle(&dev, 0);
cnrtSetCurrentDevice(dev);
cnrtQueue_t pQueue;
cnrtCreateQueue(&pQueue);
cnrtDim3_t dim = {NUM_MULTICORE,1,1};
cnrtFunctionType_t c;
switch (core_num_) {
case 1:
c = CNRT_FUNC_TYPE_BLOCK;
printf("task type = BLOCK\n");
break;
case 4:
c = CNRT_FUNC_TYPE_UNION1;
printf("task type = UNION1\n");
break;
case 16:
c = CNRT_FUNC_TYPE_UNION4;
printf("task type = UNION4\n");
break;
default:
exit(-1);
}
std::vector input_data;
std::vector output_data;
half *data_mlu, *out_data;
CNRT_CHECK(cnrtMalloc((void**)&data_mlu, data_count * sizeof(half)));
CNRT_CHECK(cnrtMalloc((void**)&out_data, data_count * sizeof(half)));
cnrtMemcpyFloatToHalf(data_mlu, data, data_count);
cnrtNotifier_t Notifier_start;
cnrtNotifier_t Notifier_end;
cnrtCreateNotifier(&Notifier_start);
cnrtCreateNotifier(&Notifier_end);
struct timeval start;
struct timeval end;
gettimeofday(&start, NULL);
cnrtPlaceNotifier(Notifier_start, pQueue);
MishKernel_MLU270<<>>(data_mlu,out_data,data_count);//MLU执行运算
cnrtPlaceNotifier(Notifier_end, pQueue);
CNRT_CHECK(cnrtSyncQueue(pQueue));
gettimeofday(&end, NULL);
float time_use = ((end.tv_sec - start.tv_sec) * 1000000 + (end.tv_usec - start.tv_usec))/1000.0;
printf("time use: %.3f ms\n", time_use);
float* output_tmp = (float*)malloc(data_count * sizeof(float));
cnrtMemcpyHalfToFloat(output_tmp, (uint16_t *)out_data, data_count);
printf("MSE:%f \n", calc_mse(cpu_out, output_tmp, data_count));//计算MSE精度
FILE* mluOutputFile = fopen("./mluoutput.txt", "w");
FILE* cpuOutputFile = fopen("./cpuoutput.txt", "w");
for (int i = 0; i < data_count; i++) {
fprintf(mluOutputFile, "%f\n", output_tmp[i]);
fprintf(cpuOutputFile, "%f\n", cpu_out[i]);
}
fclose(mluOutputFile);
fclose(cpuOutputFile);
CNRT_CHECK(cnrtFree(data_mlu));
CNRT_CHECK(cnrtFree(out_data));
CNRT_CHECK(cnrtDestroyQueue(pQueue));
cnrtDestroyNotifier(&Notifier_start);
cnrtDestroyNotifier(&Notifier_end);
cnrtDestroy();
free(data);
free(output_tmp);
free(cpu_out);
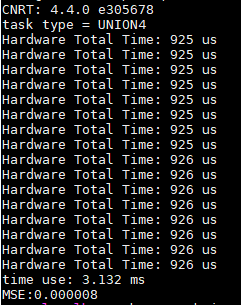
}运行结果:
热门帖子
精华帖子